
HR vs Cybersecurity: Which Career Path Offers More Opportunity in 2025?
HR vs Cybersecurity: Which Career Path Offers More Opportunity in 2025?
Two careers are at the center of today’s advanced job market: Human Resources (HR) and Cybersecurity.
Both fields are essential to the success of any modern company. HR professionals help build strong teams and maintain a healthy work culture. Cybersecurity experts protect sensitive data and defend against cyber threats.
But which career is right for you?
If you’re a graduate, career changer, or simply curious about your options, this guide breaks down everything you need to know.
From skills and salaries to job growth and day-to-day work, we compare HR vs Cybersecurity side by side. By the end, you’ll have a clear picture of both careers and which one might be the better fit for your future.

Start a Life-Changing Career in Cybersecurity Today
Why Compare HR and Cybersecurity?
Choosing the right career is more than picking a job; it’s about finding a path that matches your strengths, interests, and goals.
HR and Cybersecurity may seem worlds apart, but both are critical in today’s organizations. HR helps companies hire, train, and support employees, while Cybersecurity defends systems and data from ever-growing digital threats.
In Africa and across the globe, demand is rising for both types of professionals. Companies need strong HR teams to manage people and ensure legal compliance. At the same time, cyberattacks are on the rise, making skilled security professionals more valuable than ever.
So, how do you decide between them?
This comparison will help you weigh the pros and cons, understand what each career involves, and discover which path could offer the most opportunity for you, whether you love working with people, enjoy tech challenges, or want a career with growth and stability.
Let’s begin with a quick side-by-side view of HR and Cybersecurity.
RELATED ARTICLE: Accounting vs Cybersecurity: Everything You Need to Know
HR vs Cybersecurity: Comparison Table
Here’s a quick look at how Human Resources and Cybersecurity compare across key factors:
| Aspect | Human Resources (HR) | Cybersecurity |
| Focus | Managing employee relations, hiring, benefits, and workplace compliance. | Protecting computer systems and data from cyber threats and attacks. |
| Typical Job Roles | HR Manager, Recruitment Officer, Training Specialist, Benefits Coordinator. | Security Analyst, Network Security Engineer, Penetration Tester, Security Manager. |
| Key Skills | Communication, conflict resolution, strategic planning, people management. | Technical analysis, risk assessment, problem-solving, knowledge of IT systems. |
| Industry Demand | Steady demand across all industries for managing workforce and compliance. | Rapidly growing demand due to increasing cyber threats and digital transformation. |
| Average Salary (US) | Around $67,000 per year. | Around $133,000 per year. |
| Stress Level | Moderate to high, due to managing people, conflicts, and legal matters. | High, due to the need for constant vigilance and fast response to security threats. |
| Job Satisfaction | High for those who enjoy working with people and shaping workplace culture. | High for those who enjoy problem-solving, tech, and protecting vital systems. |
| Career Growth | Steady growth with opportunities to move into leadership (e.g., HR Director, CHRO). | Strong growth with high-level roles like Security Architect or Chief Information Security Officer (CISO). |
| Work Environment | Office-based with frequent staff interaction. | Often hybrid—office, remote, or on-site with IT teams. |
Tip: If you enjoy working closely with people, HR might be a natural fit. If you’re tech-savvy and enjoy solving complex problems, cybersecurity could be your path.
HR vs Cybersecurity: What Does an HR Professional Do?
HR professionals are at the heart of every company, managing the people who make the business work. Their job is to hire, train, and support employees, ensuring a smooth and productive workplace.
Common tasks include:
- Recruiting staff and onboarding new hires.
- Managing salaries, benefits, and leave.
- Handling employee complaints or conflicts.
- Ensuring the company follows labor laws.
- Organizing staff training and development.
In short, HR ensures that employees feel supported, motivated, and aligned with the company’s goals. They also help build a positive workplace culture, which can boost productivity and reduce turnover.
What Does a Cybersecurity Professional Do?
Cybersecurity experts are digital protectors. They guard sensitive information, prevent cyberattacks, and keep the company’s systems safe.
Common tasks include:
- Monitoring networks for suspicious activity.
- Setting up firewalls, antivirus, and security systems.
- Investigating and responding to cyber incidents.
- Training staff on security best practices.
- Ensuring the company follows data protection laws.
Their role is vital in today’s world, where one cyberattack can cost a business millions or damage its reputation. Cybersecurity professionals stay alert, adapt to new threats, and play a key role in keeping a business running securely.
Real-World Example: A small business might have an HR manager who handles hiring and staff well-being, while a cybersecurity analyst works behind the scenes to protect customer data from hackers.
READ MORE: What Coding Language is Best for Cybersecurity?
Education and Skills Needed
HR: People-Focused with a Strategic Edge
To start a career in Human Resources, most professionals have a degree in HR management, business administration, psychology, or a related field.
Common educational paths include:
- Bachelor’s Degree in Human Resources, Business, or Psychology.
- Master’s Degree for advanced roles (e.g., HR leadership, talent strategy).
In addition to formal education, certifications can boost credibility and job prospects. Two of the most recognized are:
- SHRM-CP or SHRM-SCP (Society for Human Resource Management)
- PHR or SPHR (Professional/Senior Professional in Human Resources)
Top Skills for HR:
- Communication and interpersonal skills.
- Conflict resolution and empathy.
- Strategic thinking and planning.
- Knowledge of labor laws and compliance.
Cybersecurity: Tech-Driven and Always Advancing
Cybersecurity requires a more technical background. Most professionals study computer science, information technology, or cybersecurity.
Common educational paths include:
- Bachelor’s Degree in Cybersecurity, Computer Science, or IT.
- Technical Bootcamps or Certifications for quicker entry.
Because cyber threats change constantly, continuous learning is essential. Industry-recognized certifications include:
- CompTIA Security+ – Ideal for beginners.
- CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) – For advanced roles.
- CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker) – For penetration testing and offensive security.
Top Skills for Cybersecurity:
- Understanding of networks, systems, and coding.
- Analytical thinking and attention to detail.
- Problem-solving under pressure.
- Knowledge of security tools and best practices.
Tip: HR is ideal if you love working with people and solving workplace challenges. Cybersecurity is a great fit if you enjoy tech, puzzles, and staying one step ahead of threats.
SEE ALSO: CompTIA Security Vs Google Cybersecurity Certification
Career Paths and Advancement
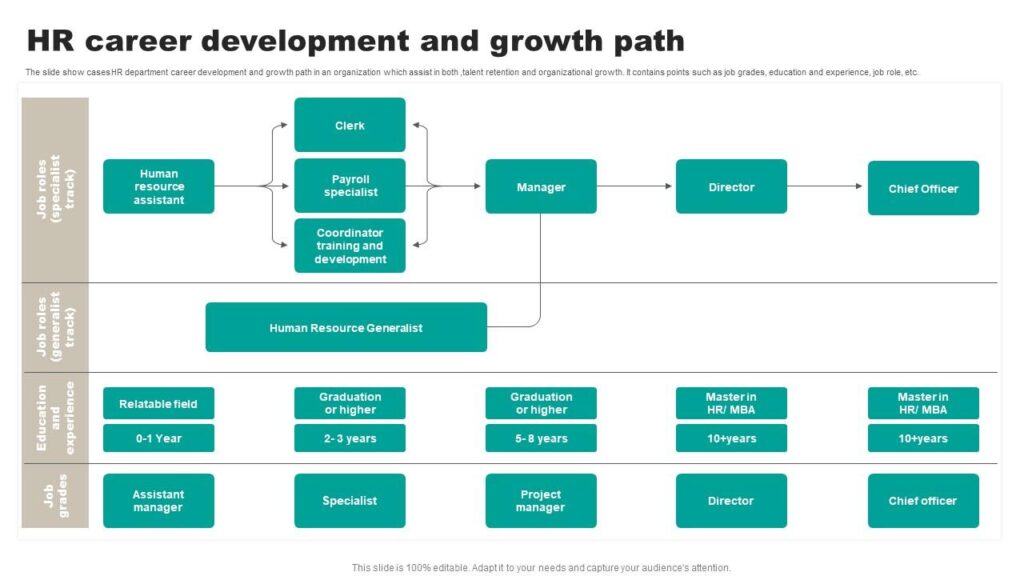
HR Career Progression
Most HR professionals begin in entry-level roles that help them understand the basics of workforce management.
Common Entry-Level Roles:
- HR Assistant
- Recruitment Coordinator
- Payroll Specialist
With experience and additional certifications, professionals can move into mid-level roles like:
- HR Manager
- Training and Development Officer
- Employee Relations Specialist
At the top of the ladder, HR professionals can take on leadership roles such as:
- HR Director
- Chief Human Resources Officer (CHRO)
These senior roles involve strategic planning, policy development, and aligning HR goals with business objectives.
How to Advance:
- Gain certifications like SHRM-SCP or SPHR.
- Develop leadership and strategic planning skills.
- Stay current with labor laws and HR tech tools.
Cybersecurity Career Progression
Cybersecurity professionals also start with foundational roles that focus on protecting systems and identifying vulnerabilities.
Common Entry-Level Roles:
- Security Analyst
- Network Administrator
- IT Support with Security Focus
As skills grow, they can move into advanced roles such as:
- Security Engineer
- Penetration Tester
- Security Consultant
Top-level positions include:
- Security Architect
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)
These roles involve designing security systems, managing teams, and setting company-wide security policies.
How to Advance:
- Earn certifications like CISSP or CEH.
- Build experience with real-world security tools.
- Stay updated on the latest cyber threats and trends.
Key Point: HR offers growth into people management and organizational leadership. Cybersecurity opens paths to technical mastery and high-stakes digital defense.
MORE: How to Become a GRC Analyst?
Challenges and Rewards
HR: Balancing People, Policies, and Emotions
Challenges:
- Handling sensitive employee issues like conflicts or complaints.
- Navigating changing labor laws and ensuring compliance.
- Balancing company goals with employee needs.
- Managing stress during layoffs, restructuring, or crises.
HR professionals must often make tough decisions that impact people directly. They need emotional intelligence, patience, and a strong grasp of policies.
Rewards:
- Shaping workplace culture and boosting morale.
- Helping employees grow through training and development.
- Playing a key role in business strategy.
- Building strong teams that drive company success.
Many HR professionals find satisfaction in creating a positive work environment and seeing their efforts lead to happier, more productive employees.
Cybersecurity: High Stakes, High Impact
Challenges:
- Staying ahead of constantly evolving cyber threats.
- Responding quickly to incidents or breaches—often under pressure.
- Managing complex systems and sensitive data.
- Dealing with long hours during security emergencies.
Cybersecurity work can be intense, requiring focus, problem-solving, and quick decision-making. The stakes are high, but so is the sense of responsibility and achievement.
Rewards:
- Protecting valuable data and digital systems.
- Being a key player in keeping a company safe.
- Opportunities to specialize in areas like ethical hacking or risk analysis.
- Strong job security and competitive pay.
Cybersecurity professionals often take pride in being the first line of defense in the digital world, and knowing their work prevents serious damage.
HR challenges are often people-focused, while cybersecurity challenges are tech-driven. Both offer meaningful rewards, whether through employee impact or digital protection.
SEE: Is Cybersecurity Hard to Learn? A Complete Analysis
Job Market and Outlook
HR: Steady Demand in Every Industry
Human Resources remains a core function in businesses of all sizes. From startups to multinational corporations, every company needs HR professionals to manage people and ensure compliance.
Current Trends:
- Growing need for HR tech skills (e.g., using HR software for hiring or payroll).
- Rise of remote work is creating demand for virtual HR support and digital engagement tools.
- Companies are focusing more on employee well-being, diversity, and inclusion, boosting the need for HR strategy.
Job Outlook:
- The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects steady growth for HR roles.
- Global demand is expected to remain strong, especially in sectors like healthcare, tech, and education.
Tip: HR is a good fit if you want a stable, people-oriented career with opportunities across many industries.
Cybersecurity: Rapid Growth and Talent Shortage
Cybersecurity is one of the fastest-growing fields worldwide. With more data moving online, businesses are investing heavily in digital protection.
Current Trends:
- Rise in cyberattacks is driving urgent demand for skilled security professionals.
- Cloud computing, remote work, and mobile apps increase security risks, and job opportunities.
- Governments and businesses are tightening data protection rules, requiring more cybersecurity compliance experts.
Job Outlook:
- The U.S. expects 31% growth in cybersecurity jobs by 2029, far above average.
- There’s a global shortage of qualified cybersecurity talent, estimated at over 3 million unfilled roles.
- High salaries and remote work options make cybersecurity especially attractive.
Tip: Cybersecurity offers strong job security, high pay, and room for rapid growth, especially for tech-savvy professionals.
READ ON: Cybersecurity Jobs: A Comprehensive Guide for Aspiring Professionals
Technology’s Impact on HR and Cybersecurity
HR: Smarter Tools for People Management
Technology has reshaped how HR professionals work. Many routine tasks, like payroll, recruitment, and employee records, are now automated using HR software.
Key Changes:
- HR Tech Platforms like BambooHR or Workday streamline hiring, onboarding, and performance reviews.
- Data Analytics help HR teams track employee satisfaction, turnover, and productivity.
- Remote Tools allow HR to manage virtual teams, conduct online interviews, and host virtual training.
This shift allows HR professionals to focus less on paperwork and more on strategy, like improving workplace culture or planning for future workforce needs.
Example: A company might use software to automatically send job offers, manage leave requests, and collect feedback, all while HR focuses on improving employee engagement.
Cybersecurity: A Constant Tech Race
In cybersecurity, technology is both the battlefield and the defense system. As cybercriminals develop new tools, cybersecurity experts must stay one step ahead.
Key Changes:
- AI and Machine Learning are now used to detect unusual activity and stop attacks in real time.
- Cloud Security is a growing focus, as more companies store data online.
- Automation helps teams respond quickly to threats without human delay.
However, tech evolution also means new threats. Cybersecurity professionals must continuously learn and adapt to protect systems effectively.
Example: A cybersecurity team may use AI to scan millions of network logs for threats, while also setting up automated alerts and quick-response systems.
Bottom Line: In HR, tech helps professionals work smarter. In cybersecurity, tech is both the tool and the challenge, making it a fast-paced, ever-evolving field.
Which Career Suits You?
Deciding between HR and Cybersecurity isn’t just about job titles; you have to show you’ve got the interest, strength, and goal. Here’s how to figure out which path could be right for you.
Choose HR If You:
- Enjoy working with people and solving workplace challenges.
- Like planning, organizing, and improving team performance.
- Are good at communication, empathy, and handling sensitive issues.
- Want a career with steady demand across many industries.
- Prefer a role focused on culture, strategy, and people development.
Example: If you enjoy helping others grow, managing conflict, or shaping a positive work environment, HR offers a meaningful and people-focused path.
Choose Cybersecurity If You:
- Love technology and solving complex problems.
- Are detail-oriented, analytical, and enjoy learning new tools.
- Thrive in fast-paced, high-stakes situations.
- Want strong job security, high earning potential, and career growth.
- Are excited about defending digital systems and staying ahead of threats.
Example: If you’re curious about how systems work and enjoy staying ahead of tech trends, cybersecurity can offer a rewarding, dynamic career.
Think Long-Term:
- HR can lead to roles like HR Director or CHRO, influencing business strategy at the highest level.
- Cybersecurity can take you to roles like Security Architect or CISO, protecting critical data and leading digital defense teams.
Tip: Reflect on what energizes you, interacting with people or working with technology, and where you see yourself making the most impact.
Conclusion
Both HR and Cybersecurity are vital careers in today’s world, and each offers unique opportunities for growth, impact, and success.
HR professionals shape the people side of business. They build strong teams, improve workplace culture, and ensure companies run smoothly and legally. Cybersecurity professionals guard the digital frontlines, protecting sensitive data and defending systems from ever-evolving cyber threats.
Your choice comes down to what drives you. If you enjoy working with people, solving workplace challenges, and leading team success, HR could be your path.
If you’re tech-savvy, love problem-solving, and want to protect systems in a fast-paced field, cybersecurity may be the better fit.
Both careers offer room to grow, chances to specialize, and the satisfaction of making a real difference.
So, what’s next for you? Take time to reflect, explore training options, and connect with professionals in both fields. Whether you choose HR or Cybersecurity, the future is full of opportunity.
FAQ
What job is close to HR?
Several roles are closely related to Human Resources and involve similar skills in people management, strategy, and compliance. Some of these include:
Talent Acquisition Specialist – Focuses specifically on hiring and recruitment.
Training and Development Coordinator – Designs and delivers employee learning programs.
Employee Relations Manager – Handles workplace issues, conflict resolution, and employee engagement.
Compensation and Benefits Analyst – Manages salary structures, bonuses, and benefit plans.
Organizational Development Consultant – Helps improve company structure, culture, and processes.
These roles are ideal if you enjoy working with people and want to support workforce success in different ways.
What is the hardest job in cybersecurity?
The most challenging jobs in cybersecurity often involve high responsibility and complex problem-solving. Some of the hardest include:
Penetration Tester (Ethical Hacker) – Requires deep knowledge of systems and creative thinking to find vulnerabilities before hackers do.
Security Architect – Designs secure IT infrastructures from scratch, which demands both technical mastery and big-picture planning.
Incident Response Manager – Handles cyberattacks in real-time, often under intense pressure to stop threats and minimize damage.
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) – Balances leadership, strategy, and risk management while being accountable for all security outcomes.
These roles are demanding but also come with high salaries and significant influence within an organization.
Is studying cybersecurity worth it?
Yes, studying cybersecurity is worth it for many reasons:
High Demand – Companies across all industries need cybersecurity experts, and there’s a global talent shortage.
Strong Salaries – Cybersecurity roles often offer above-average pay, even at entry level.
Career Growth – There are many paths to specialize in areas like ethical hacking, cloud security, or compliance.
Impactful Work – You’ll be protecting valuable data, systems, and even national security in some roles.
