
How to Become a Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) in 2025
How to Become a Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) in 2025
The future of cybersecurity is in the cloud. Every day, businesses around the world migrate sensitive operations to platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. But as they scale into these digital environments, they open themselves to a new breed of risks, ransomware attacks, data leaks, misconfigured storage, insider threats, and third-party exposure.
This shift has created one of the most urgent demands in the cybersecurity space: professionals who can protect cloud environments from the inside out.
That’s where the Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) certification stands out. Designed by (ISC)², a globally recognized leader in cybersecurity training and standards, the CCSP is not just another line on your résumé; it’s a technical passport into the growing world of secure cloud infrastructure.
Unlike traditional security roles that focus on on-premise protection, CCSP-certified professionals are trained to think cloud-first:
- How do you encrypt sensitive data in multi-tenant environments?
- How do you build secure CI/CD pipelines in DevOps?
- How do you ensure compliance with laws like GDPR when everything is hosted remotely?
As cyber threats evolve, so must your skillset. And that’s what makes CCSP a future-proof move; it aligns your skills with where the digital world is going.
In this guide, you’ll find everything you need to know about becoming a Certified Cloud Security Professional, from understanding the certification itself to preparing for the exam and unlocking career opportunities after passing.
Let’s walk through the path to becoming a standout expert in cloud security.

Start a Life-Changing Career in Cybersecurity Today
What Is the Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP)?
The Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) is a globally recognized certification awarded by (ISC)², one of the most trusted authorities in cybersecurity education. But it’s more than just a certificate; it’s a validation of your ability to design, manage, and secure cloud infrastructures across global platforms.
As more organizations adopt cloud-native technologies, the security landscape has shifted. Firewalls and perimeter-based defenses are no longer enough. Today, cybersecurity professionals must understand how to safeguard sensitive data across cloud environments, whether hosted on Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud.
That’s the gap CCSP is designed to fill.
Unlike general cybersecurity certifications, CCSP is laser-focused on cloud security. It covers a wide range of skills and responsibilities:
- Designing secure cloud architectures
- Managing cloud data lifecycle protections
- Enforcing identity and access controls in multi-tenant environments
- Ensuring compliance with data privacy laws like GDPR, HIPAA, and NDPR
- Responding to cloud-specific threats such as misconfigurations, insecure APIs, or account hijacking
In short, CCSP equips you with both the strategic and technical capabilities to manage cloud security end to end, from policies and frameworks to real-world incident handling.
What Makes CCSP Stand Out?
While many cloud certifications are vendor-specific (like AWS Certified Security – Specialty or Azure Security Engineer Associate), CCSP is vendor-neutral. This means you’re not learning to secure just AWS or just Azure—you’re trained to apply best practices across all major cloud platforms.
And that’s what employers want: someone who can adapt and lead cloud security strategy regardless of which technology stack is being used.
RELATED: How Long Does It Take to Learn Cybersecurity?
Who Should Consider Getting the CCSP Certification?
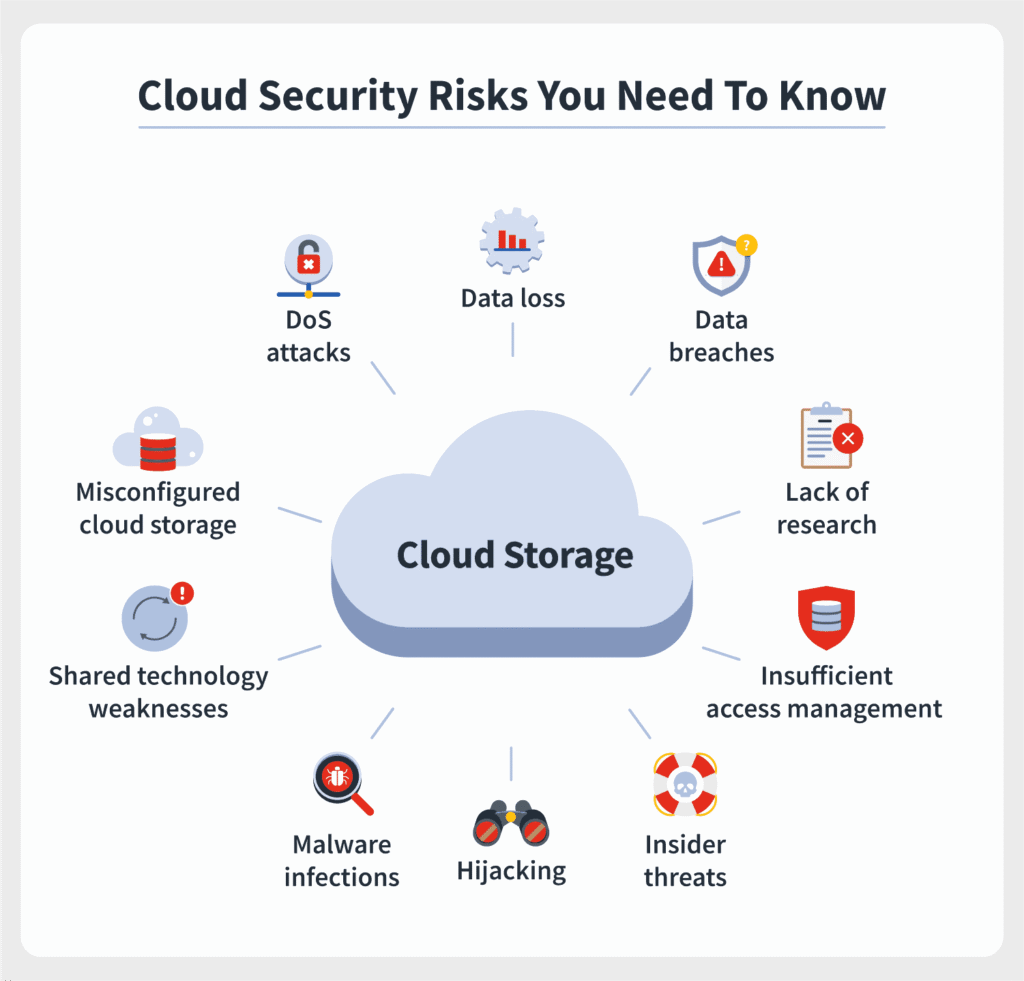
The CCSP certification isn’t just for security engineers; it’s for any professional who works with cloud technology and wants to lead in protecting it.
Whether you’re designing infrastructure, managing risk, or overseeing compliance, CCSP gives you the credibility and skills to take charge of cloud security in a professional setting.
Here’s a closer look at who would benefit the most:
1. Mid-Level Cybersecurity Professionals
If you already have some experience in information security, especially with cloud environments, CCSP helps formalize your knowledge into a globally recognized credential. It’s a natural progression after entry-level certifications like CompTIA Security+ or even after general certifications like CISSP if you want to go deeper into cloud security.
2. Cloud Engineers and Architects
Already working in cloud development or infrastructure? The CCSP helps you design cloud systems with security baked in, not just bolted on. This is critical if you’re responsible for building or migrating systems into IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS platforms.
3. Risk and Compliance Professionals
As data regulations get stricter, risk managers and compliance analysts are expected to understand the security and legal implications of cloud use. CCSP equips you with the frameworks, controls, and compliance standards to guide policy decisions and protect data sovereignty.
4. DevOps and IT Operations Staff
DevOps roles now involve heavy interaction with APIs, automation pipelines, and infrastructure-as-code tools. CCSP helps DevOps engineers avoid misconfigurations, protect CI/CD workflows, and implement secure DevSecOps practices across the board.
5. Freelancers and Consultants
Working independently or for clients? CCSP boosts your authority and positions you as a trusted expert in one of the highest-paying segments of cybersecurity, cloud security consulting.
READ ALSO: CompTIA Security Vs Google Cybersecurity Certification
Benefits of Getting CCSP Certified
Becoming a Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) isn’t just about adding letters after your name, it’s about positioning yourself where the job market is heading.
As more organizations adopt multi-cloud and hybrid environments, they need professionals who don’t just understand security, but who understand security in the cloud. That’s exactly what CCSP proves.
1. Global Recognition of Your Expertise
The CCSP is offered by (ISC)², the same organization behind the CISSP. That alone gives it industry credibility. It’s globally recognized as a gold-standard credential for cloud security, so no matter where you work, the certification speaks for you.
Employers understand that if you’re CCSP-certified, you’re not just familiar with the cloud; you’re qualified to design, secure, and manage complex cloud environments end-to-end.
2. Better Job Opportunities in High-Growth Roles
Holding a CCSP certification opens doors to in-demand roles such as:
- Cloud Security Architect
- Cloud Risk Analyst
- DevSecOps Engineer
- Security Consultant for Cloud Migration Projects
These are roles where companies can’t afford to make hiring mistakes. They need professionals who understand cloud-native risks and can prove it; CCSP gives you that proof.
3. Competitive Salary Advantage
CCSP-certified professionals consistently earn more than their uncertified peers. According to multiple industry salary reports:
- In the U.S., CCSP holders average $120,000–$150,000/year.
- In the UK and Canada, earnings exceed £75,000 or C$110,000/year.
- Even in emerging markets like Nigeria, certified professionals command premium rates in remote and contract roles.
When employers see the CCSP, they know you’re up-to-date, well-trained, and ready for high-level responsibilities, which often comes with higher compensation packages.
4. Distinction from Other Cybersecurity Certifications
CCSP is often compared to other popular certifications. Here’s how it stands out:
| Certification | Focus Area | Cloud-Specific? | Best For |
| CCSP (ISC²) | Cloud Security Architecture & Governance | Yes | Mid-to-senior cybersecurity roles |
| CISSP (ISC²) | Broad IT Security Domains | No | Security Managers |
| CEH (EC-Council) | Ethical Hacking & Penetration Testing | No | Offensive Security Analysts |
| Security+ (CompTIA) | Foundational Cybersecurity | No | Beginners |
| CCSK (CSA) | Cloud Security Knowledge (theory) | Yes | Entry-level cloud security awareness |
Unlike vendor-specific certificates (like AWS Security Specialty), CCSP is vendor-neutral, which gives you flexibility to work across platforms like Azure, GCP, or hybrid clouds.
5. Trust and Responsibility from Employers
Cloud breaches cost companies millions. That’s why employers are more likely to trust a CCSP-certified candidate with responsibilities such as:
- Designing secure cloud environments
- Advising on regulatory compliance
- Leading cloud security audits
- Training junior staff or implementing new policies
The CCSP shows you’re not just skilled, you’re reliable.
SEE MORE: Can You Get a Job with Google Cybersecurity Certificate? Find Out How
What You’ll Learn: The 6 Domains of the CCSP Exam
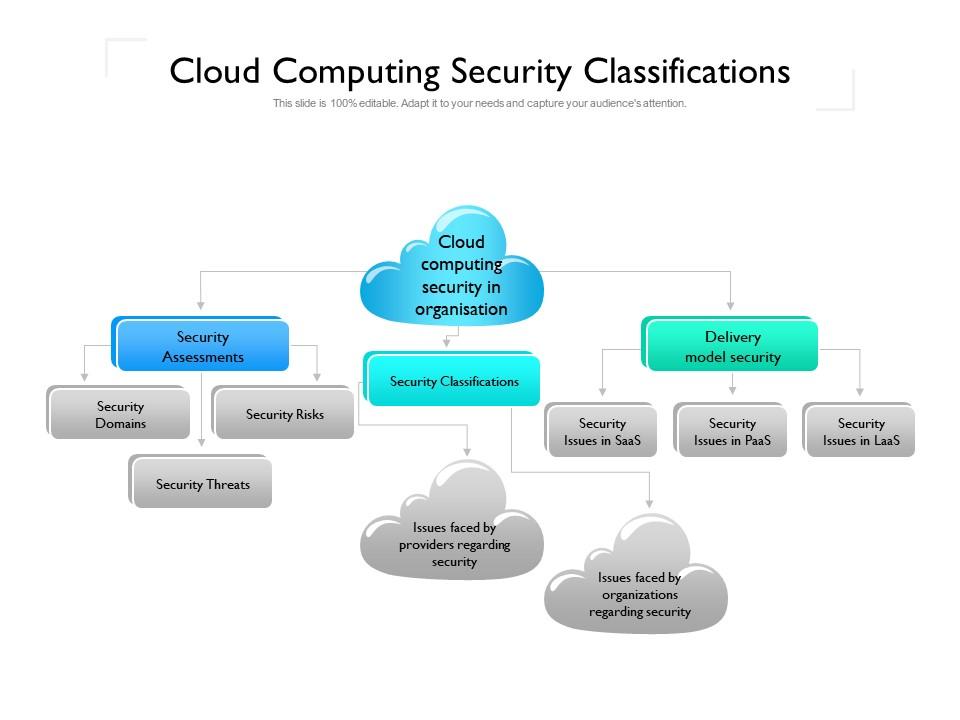
The CCSP exam isn’t just a test; it’s a blueprint for mastering cloud security. Everything you study is designed to give you practical, actionable knowledge that you can use on the job from day one.
The exam is structured around six distinct domains defined by (ISC)²’s Common Body of Knowledge (CBK). These domains reflect the real-world responsibilities of cloud security professionals, whether you’re securing data at a financial institution or protecting healthcare systems hosted on public cloud platforms.
Let’s break them down one by one:
1. Cloud Concepts, Architecture, and Design
This is where it all starts—understanding the foundation of cloud computing. You’ll learn:
- Types of cloud service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
- Deployment models (public, private, hybrid, community)
- Cloud architecture design principles
- Shared responsibility model (what you secure vs what your provider secures)
Real-world link: If your company uses AWS EC2 instances and Azure databases, this domain helps you know where your role starts and where the provider’s ends.
2. Cloud Data Security
This domain teaches you how to protect data at every stage, at rest, in transit, and in use. You’ll cover:
- Cloud data lifecycle
- Data classification and labeling
- Encryption and key management
- Data loss prevention (DLP) in cloud systems
- Data retention, deletion, and archiving policies
Real-world link: If your job involves storing customer health records in the cloud, this domain shows you how to encrypt, isolate, and manage that data securely.
3. Cloud Platform and Infrastructure Security
Here you’ll dive into the technical architecture of cloud infrastructure, including:
- Virtualization and container security
- Cloud network segmentation and isolation
- Secure configuration and hardening of cloud environments
- Disaster recovery and business continuity
Real-world link: Think securing a Kubernetes cluster, managing a multi-cloud environment, or setting up secure load balancers on GCP, this domain covers it all.
4. Cloud Application Security
This section is for those managing applications deployed in cloud environments. It focuses on:
- Secure software development lifecycle (SDLC)
- API security and secure code deployment
- Identity and access management in apps
- DevSecOps integration
Real-world link: If you’re pushing code via GitHub Actions or deploying on AWS Lambda, this domain ensures your app isn’t introducing new vulnerabilities into the environment.
5. Cloud Security Operations
Cloud environments must be monitored, updated, and defended continuously. This domain covers:
- Logging, monitoring, and alerting
- Incident response and recovery
- Change management and patching in cloud
- Forensics in cloud-based attacks
Real-world link: When a company suffers a DDoS attack on its API gateway, the knowledge from this domain helps you contain, investigate, and recover, without downtime.
6. Legal, Risk, and Compliance
This domain ties cloud security to regulations, contracts, and business impact, including:
- Legal requirements (like GDPR, NDPR, HIPAA)
- Cloud-specific audit and compliance practices
- Vendor risk management
- SLA enforcement and cloud contract terms
Real-world link: If your company processes EU customer data using U.S.-based cloud services, this domain guides you on data residency, privacy laws, and regulatory audits.
ALSO: What Is Third-Party Vendor Risk Management (TPRM)? Complete Guide
Eligibility and Requirements for CCSP
Before you invest your time and money preparing for the Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) exam, it’s important to understand the eligibility requirements. The CCSP isn’t a beginner-level certification, it’s built for professionals who already have a foundation in IT and information security.
Here’s exactly what you need to qualify, along with some tips to navigate the process if you don’t meet all the requirements yet.
Work Experience Requirements
To earn your CCSP certification, you must have:
- At least five years of cumulative, paid work experience in information technology.
- Three of those years must be in information security, and
- One of those years must be in at least one of the six CCSP domains, as defined by the CCSP Common Body of Knowledge (CBK).
Education Waiver Option
Don’t have five full years of experience yet? You might still qualify faster through a one-year experience waiver, available if you:
- Hold a four-year college degree (bachelor’s or regional equivalent), or
- Hold another credential from (ISC)²’s approved list (e.g., CISSP, CISA, Security+, CCSK, etc.)
In these cases, your required experience drops to four years instead of five.
This waiver is especially useful for professionals who transitioned to cybersecurity from adjacent fields like networking, DevOps, or compliance, but don’t yet meet the full timeline.
What Counts as Qualifying Experience?
(ISC)² has clear guidelines about the types of roles and tasks that count toward your CCSP experience. These include:
- Designing secure cloud architectures
- Managing identity and access in multi-cloud environments
- Implementing security controls in AWS, Azure, or GCP
- Writing cloud risk policies or managing audits
- Responding to cloud-related incidents or vulnerabilities
As long as your job involves protecting digital assets in cloud ecosystems, whether technical or policy-related, your experience likely qualifies.
What If You Don’t Meet the Experience Yet?
Good news: You can still take the exam and become an Associate of (ISC)².
This status allows you to:
- Pass the CCSP exam early
- Earn the experience later (you’ll have up to six years to do so)
- Start benefiting from (ISC)² resources, networks, and branding right away
This is a popular path for ambitious early-career professionals who want to signal their commitment to employers now while building experience on the job.
Summary
| Requirement | Description |
| IT Experience | 5 years total (including 3 in InfoSec and 1 in a CCSP domain) |
| Education Waiver | Reduces requirement to 4 years if you have a degree or approved cert |
| Associate Pathway | Available for those who pass the exam without full experience yet |
Meeting the eligibility requirements is your first checkpoint. Once you’re confident that your experience aligns, or you’ve planned a pathway, you’ll be ready to start preparing for the exam itself.
MORE: Vendor Risk Management (VRM) in 2025
How to Prepare for the CCSP Exam (Step-by-Step)
Passing the Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) exam takes more than just technical experience; it requires strategic preparation. This section gives you a step-by-step guide to help you prepare confidently, avoid overwhelm, and build the depth needed to pass on your first attempt.
Step 1: Understand the Exam Format
Before you open a book or start a course, know what you’re preparing for.
| Exam Component | Details |
| Total Questions | 125 (Multiple Choice) |
| Duration | 3 Hours |
| Passing Score | 700 out of 1,000 |
| Delivery | Pearson VUE Testing Centers or Online Proctoring |
| Languages | English, Japanese, and others |
The questions aren’t just theoretical; they’re scenario-based, testing your ability to apply concepts in real-world cloud security situations.
Step 2: Choose Your Study Materials
Use a mix of official and supplementary resources to cover every learning style.
Official (ISC)² Resources
- CCSP Official Study Guide (by Ben Malisow or similar authors)
- (ISC)² Official CBK (Common Body of Knowledge)
- Official Practice Tests
- Online Training Courses via (ISC)²
Recommended Third-Party Resources
- CCSP All-in-One Exam Guide by Daniel Carter
- Boson or ThorLabs Practice Exams
- YouTube Series & Study Groups
- CCSP Flashcards & Domain Summaries
Step 3: Build a Study Plan That Works
Without structure, you’ll lose momentum. Here’s a simple plan:
Week 1–2: Domain 1 (Cloud Concepts) + light reading of all domains
Week 3–4: Domains 2 & 3 (Data + Infrastructure Security)
Week 5–6: Domains 4 & 5 (Application + Ops)
Week 7: Domain 6 (Legal/Risk/Compliance)
Week 8: Full revision, practice exams, identify weak spots
Study Time Per Week: 6–8 hours minimum is ideal for working professionals.
Tip: Start with the domain that feels most familiar—this boosts early confidence.
Step 4: Join a Study Group or Mentorship Program
Studying alone can be tough. Join active online communities such as:
- Reddit’s r/ccsp or r/cybersecurity
- LinkedIn CCSP study groups
- Mentorship programs like Tolulope Michael’s GRC training, where CCSP-aligned content is taught in practical, African-friendly scenarios.
Group learning keeps you accountable, gives you perspective on difficult topics, and exposes you to real-world use cases others have encountered.
Step 5: Take Practice Exams – A Lot of Them
Practice tests train your brain to:
- Spot question traps and tricky wording
- Apply knowledge under pressure
- Improve time management
Use exams like:
- (ISC)² Official Practice Tests
- Boson CCSP Test Bank
- PocketPrep CCSP App for on-the-go quizzes
Don’t just memorize answers, understand why one option is correct and others are not.
Step 6: Prep for Exam Day
- Book your exam early at a Pearson VUE center or online (choose a quiet, reliable environment if testing from home).
- Have 1–2 rest days before the exam to refresh.
- Bring two forms of ID if testing in person.
- Review weak areas only; cramming everything last-minute is counterproductive.
Conclusion
The Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) certification isn’t just a badge; it’s a clear signal that you’re serious about leading in a cloud-first world.
With cloud technologies dominating everything from finance and healthcare to education and e-commerce, companies need professionals who can do more than react to cyber threats. They need experts who understand how to build secure cloud systems from the ground up.
By pursuing CCSP, you’re not just preparing for an exam; you’re preparing for a more secure, higher-paying, and globally relevant career.
You’ve seen what the exam involves. You’ve seen who it’s for. You’ve explored how to qualify, prepare, register, and grow beyond it.
Now the decision is yours.
If you’re ready to future-proof your career, stand out in job interviews, and contribute meaningfully to cloud security at a global level, then starting your CCSP journey is the next right move.
FAQ
How hard is the CCSP exam?
The CCSP exam is moderately difficult, especially for those without prior cloud experience. It tests not just your ability to memorize facts but your understanding of complex cloud security scenarios, policies, and implementation techniques.
Candidates report that the questions are concept-heavy and scenario-based, requiring you to apply knowledge rather than just recall it. If you’ve worked in cloud environments or have experience with cloud compliance, the exam will feel more familiar. Without hands-on exposure, it may feel abstract or theory-heavy.
Success depends on:
– Consistent study over 8–10 weeks
– Using multiple resources (books, practice exams, study groups)
– Understanding why an answer is right, not just which one
Can I learn cloud in 3 months?
Yes, but with a caveat. You can learn cloud fundamentals in 3 months if you’re consistent and focused. However, mastering cloud security to a CCSP level typically takes longer unless you already have a background in IT or cybersecurity.
In 3 months, you can:
– Understand cloud service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
– Learn how cloud platforms like AWS or Azure work
– Get familiar with basic security principles
– Start building toward more advanced concepts like identity management, encryption, and compliance in the cloud.
Many learners start with CCSK or vendor-specific beginner certifications (e.g., AWS Cloud Practitioner) within this timeframe before going for CCSP.
Is CCSP entry level?
No, CCSP is not considered entry-level. It’s designed for professionals with at least five years of experience in IT, including three in information security and one in any of the CCSP domains.
It assumes you already understand:
– Core security principles
– Risk management processes
– Cloud technologies and architecture
If you’re just starting your cybersecurity career, consider gaining experience or taking foundational certifications like:
– CompTIA Security+
– Certified Cloud Security Knowledge (CCSK)
– AWS or Azure Associate-level certs
You can still take the exam and become an Associate of (ISC)² if you don’t yet meet the full experience requirement.
Is CISSP required for CCSP?
No, CISSP is not a prerequisite for taking the CCSP exam.
However, both are offered by (ISC)², and they share a similar structure and security philosophy. Some professionals choose to take CISSP first because it covers a broader set of security domains, while CCSP is more focused on cloud security.
If you already hold a CISSP, it can:
– Make CCSP content feel easier
– Waive part of the experience requirement
– Strengthen your cloud + general cybersecurity credibility
That said, you can take CCSP independently of CISSP and still gain high value, especially if you’re working in cloud-heavy roles.
