
How Long Does It Take to Get a Cybersecurity Certificate Online?
How Long Does It Take to Get a Cybersecurity Certificate Online?
With global cybercrime damages projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, the demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals has never been higher. Organizations are under pressure to protect sensitive data, prevent costly breaches, and meet compliance obligations.
As a result, employers increasingly look for candidates who can demonstrate proven knowledge, and certifications have become one of the most recognized ways to validate those skills.
For many career changers and beginners, online cybersecurity certificates provide a flexible entry point. They can often be completed in months rather than years, making them a faster alternative to traditional degrees. The rise of free online cyber security courses with certificates, as well as affordable programs like the Google Cybersecurity Professional Certificate, has lowered the barrier to entry for those eager to join the field.
But a common question remains: How long does it take to get a cybersecurity certificate online? The answer depends on several factors, including program type, prior IT knowledge, and the time commitment you can dedicate each week.
This article breaks down the timelines of popular certification programs, strategies to accelerate your learning, and what comes after certification, including career paths and average cyber security salary expectations.

Start a Life-Changing Career in Cybersecurity Today
Why Cybersecurity Certifications Matter
Cybersecurity certifications serve as proof of competence in a field where trust and expertise are everything. Employers need assurance that candidates can protect networks, respond to incidents, and comply with regulatory frameworks. Certifications provide that assurance by validating specific technical and analytical skills.
For beginners, especially those searching for cyber security certifications for beginners or wondering how long does it take to learn cyber security for beginners, a structured certificate offers a clear starting point.
Programs such as the Google Cybersecurity Professional Certificate or CompTIA Security+ are designed to build a foundation in areas like network security, risk management, and identity access controls. These credentials help candidates stand out when applying for entry-level roles like cybersecurity analyst or SOC technician.
Another reason certifications matter is employability. A 2025 CyberSeek report shows that nearly 60% of cybersecurity job postings require at least one certification. Employers treat certificates as a baseline qualification, especially for roles that involve handling sensitive information or working within government and regulated industries. In fact, some agencies now sponsor free government cyber security training to fast-track professionals into these roles.
The financial benefits are equally compelling. According to recent labor data, certified professionals can earn a cyber security salary ranging from $75,000 to over $120,000 annually, depending on the certification level and job function. In this sense, certifications don’t just open doors; they accelerate career growth.
Whether you pursue paid or free online cyber security courses with certificates, the outcome is the same: proof that you are committed to mastering the skills required to safeguard digital systems. Certifications give you credibility, strengthen your résumé, and signal to employers that you’re prepared to contribute in one of the fastest-growing fields in technology.
RELATED: How Long Does It Take to Learn Cybersecurity?
Key Factors That Affect How Long It Takes to Get a Cyber Security Certificate
The timeline for earning an online cybersecurity certification can range from a few weeks to several months. The variation largely depends on personal circumstances and program structure. Understanding the main factors influencing completion time can help prospective students make realistic choices.
1. Program Format
Some certifications are entirely self-paced, such as the Google Cybersecurity Professional Certificate, while others follow strict schedules, like university-affiliated boot camps. A self-paced option is ideal for working professionals who want flexibility, but it may stretch the timeline if motivation is an issue. Structured programs, on the other hand, often finish faster because learners must follow weekly classes and deadlines.
2. Prior Knowledge and Experience
Beginners often ask, “How long does it take to learn cyber security for beginners?” The answer is different for everyone. Those with IT or networking backgrounds may complete certificates quickly, as they already understand core concepts. True beginners may need extra months to grasp fundamentals before moving into advanced modules. Many cyber security certifications for beginners build in introductory lessons to bridge that gap.
3. Weekly Study Commitment
Most online courses estimate timelines based on a set number of study hours per week. For instance, dedicating 10–15 hours weekly could shorten a six-month program to just three or four months. On the other hand, committing only a few hours each week may stretch even short certificates beyond a year.
4. Financial Resources
The ability to fund programs without interruptions also matters. Affordable subscriptions, like Google cybersecurity certification free trials or low-cost monthly plans, make continuous enrollment easier. More expensive boot camps may require payment plans, and financial breaks could delay progress. In some cases, learners turn to free government cyber security training initiatives to avoid cost barriers.
5. Learning Style and Resources
Students who actively use provided resources, labs, peer forums, tutoring sessions, often progress faster than those who study alone. Practical application accelerates understanding, making it easier to move through modules efficiently.
In short, the time it takes to earn a certificate is not just about the advertised duration of the program. It’s shaped by your background, study habits, and access to resources. Knowing these factors upfront will help you plan the best path toward your certification and career goals.
READ ALSO: Comptia Security+ vs Google Cybersecurity Certification: 2025 Comparison
Popular Online Certification Programs and Their Timelines
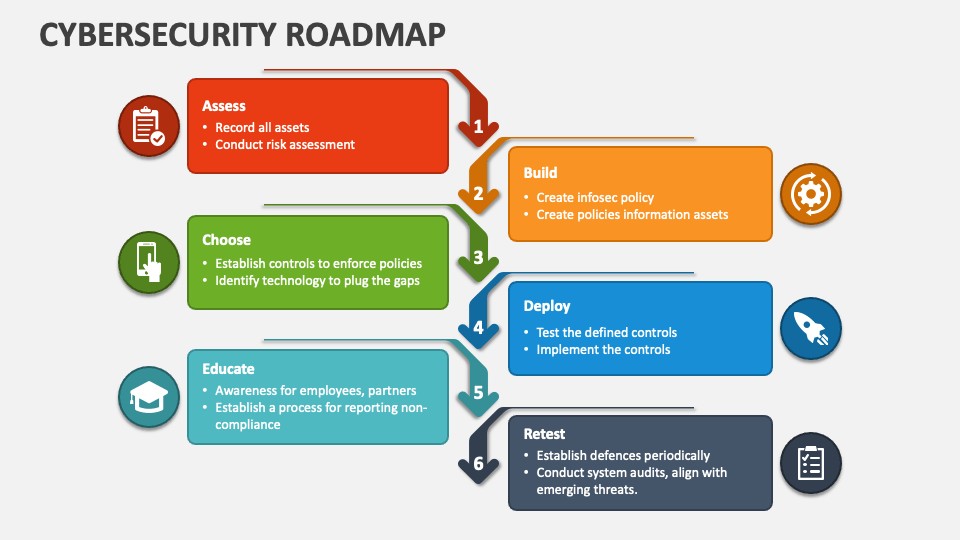
Cybersecurity is one of the few fields where certifications can open doors even without a traditional degree. With so many programs available, it’s important to understand not just the skills they offer, but also how long they typically take to complete. Below are some of the most recognized cyber security certifications for beginners and intermediate learners, along with their timelines.
1. Google Cybersecurity Professional Certificate
Duration: 3–6 months (self-paced)
Google’s entry-level program, available on Coursera, has quickly become one of the most popular starting points for beginners. It covers network security, threat analysis, and risk management through interactive labs. The average learner completes it in under six months with about 10 hours of study per week. A major draw is affordability: many learners access it through the Google Cybersecurity certification free trial, making it an accessible pathway into the field.
2. CompTIA Security+
Duration: 3–5 months
Regarded as a global standard for foundational knowledge, Security+ prepares candidates for roles such as junior security analyst or IT auditor. Most learners spend a few months preparing, especially if balancing work alongside study. It’s not free, but it is often the first professional-level certification after completing free online cyber security courses with certificates.
3. Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
Duration: 4–6 months
The CEH is a more advanced credential focused on penetration testing and ethical hacking practices. It typically requires prior IT knowledge, so beginners may need more time. Learners who dedicate at least 10–15 hours per week can finish preparation within four to six months.
4. Free Government Cyber Security Training Programs
Duration: Varies (4 weeks to 6 months)
Several government initiatives provide no-cost training for aspiring professionals. For example, Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) offers short courses that can be completed in a few weeks, while others run longer intensive boot camps. These programs are valuable for individuals looking to minimize costs while gaining credentials that employers recognize.
5. Google Cybersecurity Certification (Advanced Modules)
Duration: 3–4 months
Beyond the entry-level program, Google offers specialized modules that can be stacked for more advanced knowledge. For learners exploring both foundational and intermediate skills, completing these add-ons may extend the timeline but significantly enhance employability.
6. University-Affiliated Boot Camps
Duration: 6–9 months
Many universities partner with online learning platforms to deliver boot camps that combine live instruction with hands-on labs. While these programs are more intensive, they tend to have higher completion rates because of their structure and accountability.
7. Other Free Online Options
Duration: 2–4 months
Platforms like FutureLearn, Cybrary, and OpenLearn offer free online cyber security courses with certificates that can often be completed in a few months. These courses are best suited for beginners who want to test the waters before investing in paid programs.
Which Program Is Right for You?
If you’re just starting out, a short program like the Google Cybersecurity Professional Certificate or a government-backed free training course provides a solid entry point. More advanced learners aiming for roles in penetration testing or network defense may pursue CEH or Security+.
No matter the path, the key is to align the certificate with your career goals and timeline. For some, the fastest option may be a free short course to land an entry-level role. For others, investing several months in globally recognized certifications leads to higher salaries and broader career mobility.
SEE MORE: Can You Get a Job with Google Cybersecurity Certificate? 2025 Update
Strategies to Accelerate Certification Timelines

One of the most common questions for career changers is: “How long does it take to get a cyber security certificate?” While most programs advertise their estimated durations, the reality is that learners can often finish faster with the right approach. Here are proven strategies to help shorten your timeline without compromising mastery of the material.
1. Commit to Consistent Study Hours
Setting a fixed weekly study schedule dramatically improves progress. Learners who dedicate 10–15 hours per week to programs such as the Google Cybersecurity Professional Certificate often complete them in three to four months instead of the typical six. Consistency is more effective than occasional long sessions.
2. Use Practice Labs and Simulations
Practical application accelerates understanding. Many online certifications provide sandbox environments where you can practice real-world scenarios like phishing detection or network defense. By actively engaging with these labs, students move through modules faster and retain knowledge better.
3. Leverage Free and Supplemental Resources
Pairing paid programs with free online cyber security courses with certificates can reinforce concepts without additional cost. Similarly, tapping into free government cyber security training provides extra practice opportunities that complement formal certificates. This multi-resource approach can reduce time spent revisiting difficult topics.
4. Join Study Communities
Peer support keeps learners motivated and accountable. Online forums, LinkedIn groups, and Discord communities dedicated to certifications like Security+ or CEH can provide quick answers to questions that might otherwise slow progress.
5. Focus on Entry-Level First
Beginners sometimes get overwhelmed by advanced certifications. Starting with cyber security certifications for beginners, such as Google Cybersecurity or CompTIA Security+, creates momentum and confidence. Once foundational knowledge is in place, higher-level credentials become easier and quicker to achieve.
6. Explore Flexible Learning Options
If affordability is a concern, many platforms now offer monthly subscriptions or Google Cybersecurity certification free trials, allowing learners to complete programs in shorter bursts without financial strain. Committing to an intensive month of study during a free trial can save time and money.
7. Apply What You Learn Immediately
Integrating concepts into your current job, freelancing, or volunteering for nonprofit organizations provides real-world context. Learners who practice daily often complete courses in half the time compared to those who only study theoretically.
Whether you’re balancing a full-time job or diving in full-time, strategies like consistency, leveraging free resources, and choosing beginner-friendly certificates first can drastically shorten the path to becoming certified.
ALSO READ: Phishing Attacks: Types, Examples, and How to Prevent Them
What Comes After Certification: Career Opportunities and Salaries
Earning a cybersecurity certificate is more than just an academic achievement, it’s a launchpad for real career opportunities. Once learners complete their chosen program, the next step is translating those skills into tangible roles and income.
1. Entry-Level Job Roles
For those completing cyber security certifications for beginners such as the Google Cybersecurity Professional Certificate or CompTIA Security+, the most common pathways include roles like:
- Security Analyst
- SOC (Security Operations Center) Technician
- IT Support Specialist with a security focus
These positions provide hands-on experience monitoring threats, analyzing logs, and assisting with compliance, forming the foundation for more advanced roles.
2. Mid-Level and Specialized Careers
With additional certifications such as CEH or CISSP, professionals can move into specialized paths like penetration testing, compliance management, or cloud security. Many learners who start with free government cyber security training eventually progress to these higher-paying, niche roles.
3. Salary Potential
One of the biggest motivators for pursuing a certificate is earning power. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median cyber security salary for analysts was about $120,000 in 2025. Entry-level positions often start around $75,000, while advanced certifications and experience can push salaries above $150,000.
Even in developing regions, certifications significantly boost income potential. For instance, professionals in Africa who complete globally recognized certificates often earn double the national IT average.
4. Career Growth Beyond Certificates
Certification is only the beginning. Pairing credentials with practical experience, whether through internships, freelance work, or volunteering, accelerates upward mobility. Employers value candidates who can demonstrate applied skills as much as theoretical knowledge.
5. Continuous Learning
Cybersecurity is a rapidly evolving field. New threats and technologies emerge daily, which means professionals must keep updating their knowledge. Many who start with a single certificate eventually return for advanced courses, such as cloud security or governance and compliance, to stay competitive.
In short, certifications open the door to high-demand jobs with strong earning potential. They provide the credibility to secure entry-level roles, while also laying the foundation for advanced, high-paying careers in cybersecurity.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity certifications remain one of the most practical ways to break into or advance within the security field. The time it takes to earn a certificate varies, from a few weeks for short free government cyber security training courses to six months or more for structured programs like the Google Cybersecurity Professional Certificate or CompTIA Security+.
Factors such as prior knowledge, study commitment, and chosen program format will shape your journey. But one thing is certain: whether you pursue cyber security certifications for beginners or advanced credentials, these certifications unlock access to a booming job market with attractive salaries and growth potential.
For those just starting, focus on beginner-friendly options and consistent study habits. Over time, stack certifications and build practical experience to move into higher-paying and more specialized roles.
Cybersecurity is not just a career choice; it’s a commitment to continuous learning in a field that protects businesses, governments, and individuals worldwide.
FAQ
Can I take certified in cybersecurity online?
Yes. Many recognized certification bodies now offer online pathways. For example, the Google Cybersecurity Professional Certificate is 100% online, while CompTIA allows you to take exams remotely with proctoring. This flexibility makes it possible to prepare, practice, and get certified without ever stepping into a classroom.
How much does a cyber security certificate cost?
Costs vary widely depending on the program. Short online courses may cost nothing if you choose free online cyber security courses with certificates, while professional certifications like CompTIA Security+ typically cost around $370–$450 for the exam. More advanced credentials such as CISSP or CEH can range from $700 to over $1,000, excluding study materials or training boot camps.
Is 40 too old to start a career in cyber security?
Not at all. Cybersecurity values skills, critical thinking, and problem-solving over age. Many people transition into the field in their 30s, 40s, or even 50s. In fact, having prior career experience, whether in IT, risk management, compliance, or another industry, can make you especially valuable for certain roles.
Does cyber security have a future?
Absolutely. Cybersecurity is one of the fastest-growing industries globally. With rising threats like ransomware, phishing, and data breaches, demand for qualified professionals continues to outpace supply. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects cybersecurity roles will grow by over 30% in the next decade, ensuring long-term career stability.
