
Cybersecurity vs Cloud Computing: A Comprehensive Comparison
Cybersecurity vs Cloud Computing: A Comprehensive Comparison
In the digital age, cybersecurity and cloud computing are two essential tools for businesses. Virtual reality is quickly becoming the norm, and the protection of virtual reality is completely dependent on information and technology security. Safeguarding and storing data is needed now more than ever. By investing in these two areas, businesses can ensure that their data is safe and secure.
In storing data, two fields stand out for their critical importance in shaping the digital economy: cybersecurity and cloud computing. These two, while distinct, are important to businesses who want to navigate the complexities of the digital landscape.
Cybersecurity focuses on safeguarding data, systems, and networks from increasing cyber threats, while cloud computing delivers scalable and efficient solutions to store and manage data over the internet.
As organizations increasingly depend on technology, professionals skilled in these areas are in high demand. Which brings about the question: which path offers the best career prospects? Understanding the similarities and differences between these fields is vital to making an informed decision.
Whether you’re drawn to the challenge of fending off cyberattacks or the innovative opportunities in cloud solutions, this article will help you explore both paths and decide which aligns better with your interests and goals.

Start a Life-Changing Career in Cybersecurity Today
READ ALSO: Cybersecurity vs Devops Salary: Everything You Need to Know
What Is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is the practice of defending networks, systems, and data from malicious attacks. As our reliance on digital tools grows, so does the sophistication of cyber threats. Cybersecurity professionals work tirelessly to counteract breaches, safeguard sensitive information, and ensure the integrity of digital infrastructures.
The scope of cybersecurity is vast, encompassing domains such as:
- Network Security: Protecting the infrastructure that facilitates communication between systems.
- Application Security: Ensuring the safety of software from vulnerabilities like injections or cross-site scripting.
- IoT Security: Addressing risks associated with interconnected devices.
- Zero-Trust Models: A security framework emphasizing verification and micro-segmentation.
With the rise of cyberattacks, the role of cybersecurity has evolved to include proactive threat detection and management. Cybersecurity professionals utilize tools such as firewalls, encryption protocols, and penetration testing techniques to protect digital ecosystems.
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing revolutionizes how businesses access and utilize computational resources. Instead of investing in expensive infrastructure, organizations leverage cloud services to store, manage, and process data.
Key components of cloud computing include:
- SaaS (Software as a Service): Delivering applications over the internet without requiring local installation.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): Offering a platform to developers for building, testing, and deploying applications.
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): Providing fundamental computing resources such as storage and networking.
- Serverless Computing: Allowing developers to focus on coding while the cloud provider manages the infrastructure.
Cloud computing’s benefits are undeniable. It provides businesses with scalability, cost-efficiency, and accessibility, making it a cornerstone of modern IT strategies. However, as organizations shift their operations to the cloud, the need for robust cloud security also becomes paramount, further intertwining these two domains.
Summary Table: Cybersecurity vs Cloud Computing
| Aspect | Cybersecurity | Cloud Computing |
| Definition | Protects systems, networks, and data from cyber threats. | Delivers scalable IT resources and services over the internet. |
| Key Focus | Security of systems, data integrity, and threat prevention. | Infrastructure scalability, automation, and service delivery. |
| Common Roles | Cybersecurity Analyst, Ethical Hacker, Incident Responder, CISO. | Cloud Engineer, Cloud Architect, DevOps Engineer, Cloud Consultant. |
| Top Certifications | CISSP, CISM, CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker). | AWS Solutions Architect, Microsoft Azure Fundamentals, Google Professional Cloud Architect. |
| Salary Ranges | $85,000–$200,000+ (CISO and senior roles higher). | $90,000–$180,000+ (higher for specialized roles like Cloud Architect). |
| Learning Curve | Requires strong analytical skills, knowledge of networks, systems, and evolving threats. | Involves programming basics, cloud platform expertise, and understanding infrastructure management. |
| Ease of Entry | Moderate—requires foundational knowledge of cybersecurity principles and IT systems. | Moderate—requires familiarity with cloud platforms and programming concepts. |
| Overlap/Intersection | Both fields focus on securing data and infrastructure. | Cloud Security (a subset of cybersecurity) ensures safety within cloud environments. |
| Job Market Growth | High demand with projected growth of 35% in the next decade. | Strong growth of 25%-30% due to increasing cloud adoption. |
| Which Pays More? | Comparable salaries, with senior cybersecurity roles (e.g., CISO) often commanding top earnings. | High-paying roles in cloud architecture and hybrid fields like cloud security. |
| Ideal for Those Who | Enjoy solving security challenges, analyzing threats, and protecting data integrity. | Prefer designing and managing scalable systems, and leveraging cloud-based solutions. |
| Long-Term Stability | Highly stable due to constant evolution of cyber threats. | Promising with opportunities to specialize in cutting-edge technologies like serverless computing. |
SEE MORE: How Long Does It Take to Learn Cybersecurity?
Key Similarities and Differences: Cybersecurity vs Cloud Computing
While cybersecurity and cloud computing serve different purposes, they often intersect in their shared goal of protecting data and maintaining the efficiency of IT systems. Both rely heavily on technology and require professionals to stay updated with advancements to tackle new challenges effectively.
- Data Protection: Cybersecurity focuses on safeguarding data from unauthorized access, theft, or breaches, while cloud computing ensures data is stored securely and remains accessible across global infrastructures.
- Integrated Security Measures: Cloud platforms like AWS and Microsoft Azure incorporate cybersecurity practices, offering features like encryption, access controls, and compliance tools.
- Operational Necessity: Both fields are critical to businesses. Without cloud computing, scalability and innovation would falter; without cybersecurity, businesses would be vulnerable to attacks, undermining trust and continuity.
Distinct Objectives and Approaches
Despite their overlap, the core objectives of cybersecurity and cloud computing differ significantly:
- Cybersecurity: Primarily concerned with preventing unauthorized access, ensuring compliance, and mitigating risks. Tools like intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and ethical hacking are central to this domain.
- Cloud Computing: Focuses on delivering on-demand resources, improving productivity, and supporting innovation. Technologies like virtualization and APIs play a crucial role in providing these services.
Toolsets and Techniques
When comparing cybersecurity and cloud computing, understanding their respective toolsets and techniques provides valuable insight into how professionals operate in these fields and address challenges.
Cybersecurity: Core Tools and Techniques
Cybersecurity focuses on safeguarding digital assets, systems, and networks from threats. The field employs a diverse set of tools and methodologies to identify, prevent, and respond to cyber risks effectively. Key tools and techniques include:
- Encryption: This technique ensures data confidentiality by converting information into an unreadable format for unauthorized users. Advanced encryption standards (AES) and RSA are commonly used.
- Firewalls: Acting as a barrier, firewalls monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on security rules, preventing unauthorized access to systems.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): These tools identify potential threats in real time, enabling quick responses to mitigate risks.
- Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing: Professionals use ethical hacking methods to test vulnerabilities within a system, simulating potential cyberattacks to identify weak points.
- SIEM Tools (Security Information and Event Management): Tools like Splunk and LogRhythm aggregate and analyze security data, providing insights to detect anomalies and security breaches.
- Antivirus and Malware Analysis Tools: These help detect, quarantine, and remove malicious software while analyzing their behavior for future prevention.
OTHERS LIKE THIS: The Impact of Quantum Computing on Cybersecurity
Cloud Computing: Core Tools and Techniques
Cloud computing emphasizes delivering scalable, on-demand computing resources over the internet. Professionals in this domain rely on tools that enable resource management, application development, and efficient deployment. Key tools and techniques include:
- Virtualization: A cornerstone of cloud computing, virtualization allows multiple virtual systems to operate on a single physical system, optimizing resource use. Popular virtualization tools include VMware and Hyper-V.
- Application Programming Interfaces (APIs): APIs facilitate communication between software applications, enabling seamless integration of cloud services with other systems.
- Cloud-Based Services:
- SaaS (Software as a Service): Delivers software applications via the cloud (e.g., Google Workspace, Salesforce).
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): Provides a platform for developers to build and deploy applications (e.g., Heroku, Google App Engine).
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): Offers virtualized computing resources over the internet (e.g., Amazon EC2, Microsoft Azure).
- Automation and Orchestration Tools: Platforms like Terraform and Kubernetes streamline the deployment and management of cloud resources.
- Cloud Security Solutions: Cloud-native security tools, such as AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Azure Security Center, ensure compliance and data protection within cloud environments.
Comparing the Toolsets
While cybersecurity tools are designed to protect and defend, cloud computing tools aim to build and scale. However, there is a notable overlap, especially in the domain of cloud security, where the need for robust data protection aligns both fields. Tools like AWS Security Hub exemplify this intersection, combining cloud functionality with advanced security measures.
Understanding these toolsets highlights the complementary yet distinct nature of cybersecurity and cloud computing, making each field integral to modern IT ecosystems.
Career Opportunities
Cybersecurity Careers
Cybersecurity professionals play an essential role in defending systems and data against threats. The demand for skilled cybersecurity experts continues to grow across industries. Key career paths include:
- Cybersecurity Analyst: Responsible for monitoring systems, identifying threats, and implementing defensive measures.
- Ethical Hacker: Also known as penetration testers, ethical hackers simulate attacks to uncover vulnerabilities in systems.
- Incident Responder: Specializes in responding to and mitigating the effects of security breaches.
- Malware Analyst: Focuses on understanding malicious software and devising strategies to counteract it.
Necessary Certifications
Certifications play a pivotal role in building credibility and expertise in the cybersecurity field. Popular certifications include:
- CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional)
- CISM (Certified Information Security Manager)
- CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker)
- CompTIA Security+
Cloud Computing Careers
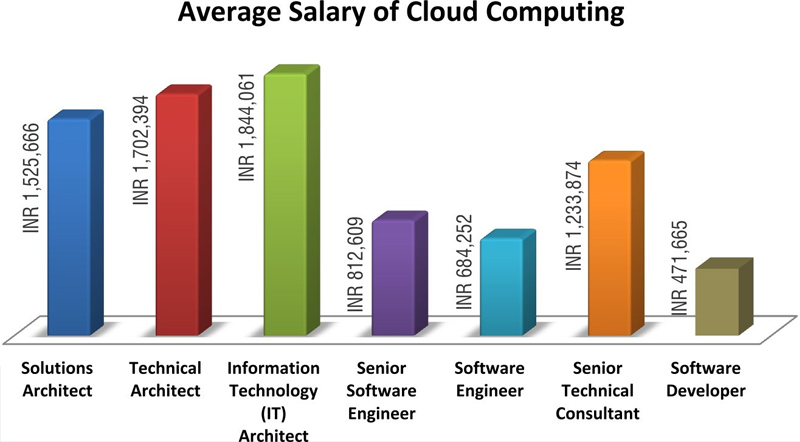
Cloud computing careers revolve around designing, implementing, and maintaining cloud-based solutions for organizations. High-demand roles in this field include:
- Cloud Engineer: Specializes in developing and managing cloud infrastructure.
- Cloud Architect: Designs and oversees cloud computing strategies for organizations.
- DevOps Engineer: Combines development and operations expertise to streamline software delivery and infrastructure management.
- Cloud Consultant: Advises businesses on cloud strategies and best practices.
Necessary Certifications
Certifications validate expertise and open doors to advanced roles in cloud computing. Top certifications include:
- AWS Solutions Architect
- Microsoft Azure Fundamentals
- Google Cloud Certified Professional Cloud Architect
- CompTIA Cloud+
Comparing Salaries
When it comes to compensation, both fields offer competitive salaries. However, roles in cybersecurity and cloud computing may vary based on specialization and experience:
- Cybersecurity Analyst: $70,000 – $120,000 annually
- Cloud Engineer: $80,000 – $130,000 annually
- Ethical Hacker: $90,000 – $140,000 annually
- DevOps Engineer: $95,000 – $150,000 annually
Professionals with hybrid skills, such as expertise in cloud security or DevOps, often command higher salaries due to their versatility.
Comparing cybersecurity vs. cloud computing salaries highlights the potential for lucrative careers in both domains, with opportunities tailored to individual strengths and interests.
SEE MORE: The Future of Cybersecurity in the Age of AI (Artificial Intelligence)
Learning Curve: Cybersecurity vs Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing vs Cybersecurity: Which Is Easy to Learn?
The learning curve for cybersecurity and cloud computing depends on a combination of foundational knowledge, practical experience, and individual aptitude. While both fields offer entry points for beginners, certain differences can influence how easy each is to learn.
Skills Required for Cybersecurity
To start in cybersecurity, individuals typically need a strong understanding of:
- Networking Fundamentals: Knowledge of protocols, firewalls, and network configurations.
- Operating Systems: Familiarity with Windows, Linux, and macOS environments.
- Programming and Scripting: Skills in languages like Python, Java, or Bash are valuable for automating security tasks and analyzing code vulnerabilities.
- Threat Analysis: The ability to identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks.
Skills Required for Cloud Computing
Entering the cloud computing domain requires proficiency in:
- Virtualization and Networking: Knowledge of virtual machines, containers, and software-defined networking.
- Programming: Familiarity with cloud-focused languages like Python, JavaScript, or Go.
- Cloud Platforms: Understanding the fundamentals of platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Skills in tools like Terraform or Ansible for automating infrastructure deployment.
Accessibility to Beginners
- Cybersecurity: Beginners may find cybersecurity more approachable due to the abundance of free online resources and hands-on labs, such as Capture The Flag (CTF) challenges and platforms like TryHackMe.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud platforms often require familiarity with specific tools and ecosystems, which can be challenging for beginners without prior technical experience.
Ultimately, the ease of learning depends on an individual’s background and interests. Those intrigued by problem-solving and defense mechanisms might prefer cybersecurity, while individuals drawn to scalable systems and resource management may gravitate towards cloud computing. Both fields offer structured learning paths, certifications, and abundant opportunities for growth.
Cybersecurity vs Cloud Computing Reddit Perspectives
Reddit serves as a hub for industry professionals and aspiring tech enthusiasts to share insights, discuss challenges, and exchange advice. Perspectives from Reddit communities often provide unfiltered and practical views on the dynamics of cybersecurity and cloud computing careers.
Challenges Highlighted on Reddit
- Cybersecurity: Discussions often emphasize the pressure and responsibility associated with safeguarding critical systems. Professionals highlight the need for constant learning due to evolving threats and technologies.
- Cloud Computing: Common concerns include the steep learning curve of mastering cloud platforms and the rapid pace of innovation, which demands continuous upskilling.
Career Opportunities
- Cybersecurity: Reddit users frequently discuss the increasing demand for roles like ethical hackers and threat analysts, especially as cyber threats grow in sophistication. Threads often recommend certifications like CISSP and CompTIA Security+ as stepping stones.
- Cloud Computing: Posts highlight the growing reliance on cloud technologies and the high demand for cloud architects and engineers. Certifications such as AWS Solutions Architect and Azure Fundamentals are often suggested.
Salary Comparisons
A recurring theme is the comparison of cybersecurity vs cloud computing salaries, with users noting competitive pay in both domains. Many threads point out that hybrid roles, such as cloud security engineers, often command premium salaries.
Reddit’s perspectives reflect real-world experiences, making it a valuable resource for individuals navigating career choices between cybersecurity and cloud computing.
AWS, Cybersecurity, and DevOps: The Intersections
The convergence of cloud computing, cybersecurity, and DevOps illustrates how these fields are interlinked, particularly in modern IT environments where seamless integration and robust security are paramount.
Cybersecurity vs Cloud Computing vs AWS
AWS (Amazon Web Services) plays a pivotal role in both cybersecurity and cloud computing domains. As one of the leading cloud providers, AWS offers an extensive suite of services that cater to scalable computing needs while incorporating robust security features. Key aspects of this intersection include:
- AWS Security Measures:
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) allows organizations to manage access permissions effectively.
- Services like Amazon GuardDuty and AWS Shield enhance threat detection and protection against distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
- AWS Key Management Service (KMS) ensures secure encryption and data protection.
- Certifications:
- AWS certifications, such as AWS Certified Security – Specialty, blend cloud computing expertise with advanced security knowledge.
- These certifications provide professionals with the credentials to manage and secure AWS environments effectively, bridging the gap between cybersecurity and cloud computing.
DevOps vs Cybersecurity Salary
DevOps, which emphasizes automation, collaboration, and efficiency in software development and operations, often overlaps with cloud computing and security roles. Salary comparisons reveal lucrative opportunities:
- DevOps Engineers: With expertise in tools like Kubernetes and CI/CD pipelines, DevOps professionals earn between $95,000 and $150,000 annually.
- Cybersecurity Professionals: Analysts and ethical hackers earn competitive salaries, ranging from $70,000 to $140,000 depending on specialization.
Hybrid roles, such as Cloud Security Engineers and DevSecOps Specialists, often command even higher salaries due to their ability to integrate security protocols within agile development environments.
OTHERS LIKE THIS: GRC Analyst vs SOC Analyst: Everything You Need To Know
Synergy Between AWS, Cybersecurity, and DevOps
The integration of AWS services within DevOps workflows demonstrates the synergy between these fields. Examples include:
- Automating infrastructure provisioning through AWS CloudFormation while embedding security best practices.
- Implementing DevSecOps strategies to ensure continuous security integration throughout the software development lifecycle.
AWS exemplifies the blending of cloud computing and cybersecurity, creating a foundation for innovative hybrid careers that are critical in today’s tech landscape.
DevOps vs Cybersecurity Salary
The rapid growth of technology has paved the way for lucrative career paths in both cybersecurity and cloud computing, particularly in roles such as DevOps engineering and cybersecurity analysis. Understanding the salary trends in these fields is crucial for anyone evaluating their potential earning potential and long-term financial security.
DevOps Salary Overview
DevOps engineers play a vital role in bridging development and operations teams, ensuring seamless integration and efficient delivery pipelines. Their skill set combines expertise in automation, cloud services, and software deployment. On average, DevOps engineers earn between $95,000 and $135,000 annually, with experienced professionals or those specializing in tools like Kubernetes or AWS often exceeding these figures.
Cybersecurity Salary Overview
Cybersecurity professionals focus on safeguarding organizations against cyber threats, ensuring data integrity, and maintaining secure systems. Key roles, such as cybersecurity analysts, ethical hackers, and incident responders, typically offer salaries ranging from $85,000 to $130,000 per year. Senior positions, like Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), can command annual salaries well above $200,000, depending on industry and experience.
Salary Comparison: DevOps vs Cybersecurity
When comparing salaries, the specifics of the role, industry, and geographic location are significant factors. For instance, DevOps engineers often see higher initial salaries due to their direct involvement in optimizing business processes, while cybersecurity roles may offer steadier salary growth as organizations increasingly prioritize security in their digital strategies.
- Entry-Level Salaries: DevOps engineers often start at $70,000-$90,000, whereas cybersecurity professionals typically begin at $65,000-$85,000.
- Specialized Roles: A cloud security analyst, a hybrid role intersecting DevOps and cybersecurity, can earn up to $150,000, demonstrating the financial benefits of cross-domain expertise.
- Long-Term Prospects: Both fields show strong salary growth trajectories, but cybersecurity might offer more stability due to the ongoing evolution of cyber threats.
By understanding these salary dynamics, aspiring professionals can align their career goals with financial aspirations and market demand.
Industry Trends and Future Prospects
The technological landscape is evolving rapidly, with cybersecurity and cloud computing emerging as cornerstones of modern IT infrastructure. Analyzing the trends shaping these fields offers valuable insights into their future trajectories and career opportunities.
Growing Reliance on Cloud Platforms and the Need for Cloud Security
As businesses increasingly adopt cloud platforms for their scalability and cost-effectiveness, securing these environments has become a top priority. Hybrid and multi-cloud strategies are gaining traction, which require robust security frameworks to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance. This convergence has led to a surge in demand for professionals skilled in both cloud computing and cybersecurity, particularly in roles like cloud security architects and cloud compliance officers.
Cybersecurity’s Expanding Role with AI, IoT, and Blockchain
Cybersecurity is evolving beyond traditional threat detection to encompass emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain. These advancements present both opportunities and challenges:
- AI is being leveraged for predictive threat analysis but also introduces risks of AI-driven cyberattacks.
- IoT devices expand the attack surface, necessitating innovative security solutions for interconnected systems.
- Blockchain offers new methods for securing transactions, but its integration into industries highlights vulnerabilities in implementation.
These developments indicate that cybersecurity will remain a high-demand field as organizations strive to address these complex challenges.
Synergy Between Cloud Computing and Cybersecurity
The interdependence of cloud computing and cybersecurity is driving the emergence of hybrid career paths. Professionals who can integrate security measures into cloud environments—such as configuring AWS or Azure security tools—are highly sought after. This synergy not only enhances career flexibility but also ensures relevance in an ever-changing job market.
Job Market Outlook
Both fields are projected to experience substantial growth:
- Cybersecurity: According to industry reports, cybersecurity job openings are expected to grow by 35% over the next decade, far outpacing many other professions.
- Cloud Computing: With cloud adoption accelerating, cloud-related roles are anticipated to grow by 25%-30%, particularly in areas like serverless computing and containerization.
These trends underscore the increasing reliance on professionals who can adapt to evolving technologies, making both fields promising choices for long-term career stability.
READ ALSO: Cybersecurity Salary: A Comprehensive Guide
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider
Choosing between cybersecurity and cloud computing as a career path depends on various factors, including job market trends, individual interests, and long-term aspirations. Here’s an in-depth exploration to help make an informed decision.
AWS or Cybersecurity: Which Is Better as a Career?
The decision often boils down to market demand and personal preferences:
- Job Market Demand: Both fields are experiencing robust growth, but their focus areas differ. Cybersecurity professionals are critical for combating evolving threats, while cloud computing experts are essential for designing scalable IT infrastructure.
- Growth Rates: Cloud computing may see faster short-term growth due to widespread digital transformation, but cybersecurity offers more stability as cyber threats remain constant.
- Hybrid Roles: AWS certifications, such as AWS Certified Security – Specialty, highlight the intersection of cloud computing and cybersecurity. Professionals who master both fields have access to highly lucrative roles like cloud security architect or DevSecOps engineer.
Personal Interests and Strengths
Your natural strengths and interests should play a significant role in your decision:
- Analytical Skills: Cybersecurity appeals to those who enjoy analyzing threats, solving complex problems, and staying ahead of cybercriminals.
- Infrastructure and Development: Cloud computing is ideal for those passionate about system design, scalability, and leveraging automation tools like Kubernetes.
- Dynamic Nature: Cybersecurity requires continuous learning due to ever-changing threats, while cloud computing emphasizes evolving technology stacks and tools.
Long-Term Stability and Opportunities
- Cybersecurity offers unmatched job security due to the critical need for protection against breaches, with roles like CISO and threat intelligence analysts offering career longevity.
- Cloud Computing provides opportunities for specialization in diverse areas like DevOps, serverless computing, and AI integration, catering to a broad range of industries.
Key Takeaway
Both careers are rewarding and in-demand, but the choice should align with your strengths, interests, and the type of impact you want to make in the tech industry. Those who can integrate skills from both fields will have a competitive advantage in the hybridized IT landscape.
Aligning Career Choices with Personal Goals and Market Demand
Aspiring professionals should consider their personal interests and strengths when choosing a career path:
- If you are passionate about combating cybercrime, maintaining system integrity, and solving complex security challenges, cybersecurity is the way to go.
- For those drawn to building, automating, and managing scalable infrastructures, cloud computing presents an exciting frontier.
Additionally, the market demand for hybrid skills, such as securing cloud environments, underscores the value of certifications and hands-on experience in both fields.
Final Advice for Aspiring Professionals
As the lines between cybersecurity and cloud computing blur, gaining foundational knowledge in both fields can open doors to specialized and high-paying roles. For instance, certifications like AWS Security Specialty, CISSP, or Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate can significantly enhance career prospects.
Ultimately, the decision should reflect your long-term career vision and willingness to adapt to the evolving tech landscape. By making an informed choice, you can position yourself for success in a dynamic and ever-growing industry.
FAQs
Which one is better, cybersecurity or cloud computing?
The answer depends on your interests and career goals:
Cybersecurity is ideal if you enjoy tackling complex security challenges, protecting data, and staying ahead of cyber threats. It offers job stability and a critical role in all industries.
Cloud Computing is better suited for those who like designing and managing scalable IT infrastructures, focusing on innovation and automation. It offers diverse opportunities across business and technology sectors.
For hybrid career paths, mastering both fields, especially cloud security, can provide the best of both worlds.
What pays more, cybersecurity or cloud computing?
Both fields offer competitive salaries, but specific roles and expertise determine earnings:
Cybersecurity: Roles like Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) and cybersecurity architects often command high salaries, ranging from $120,000 to over $200,000 annually.
Cloud Computing: Positions like cloud architects and DevOps engineers frequently offer salaries between $110,000 and $180,000, with high demand for expertise in platforms like AWS and Azure.
On average, salaries are comparable, but roles that combine cloud computing and cybersecurity, such as cloud security architects, tend to have the highest earning potential.
Is cloud computing part of cybersecurity?
Not exactly. Cloud computing and cybersecurity are separate but interrelated fields:
Cloud computing involves the delivery of IT resources and services over the internet.
Cybersecurity encompasses the protection of systems and data from threats.
However, securing cloud environments is a critical aspect of cybersecurity, often referred to as cloud security, which ensures the safety of data and applications hosted in the cloud.
Is cybersecurity the same as cloud security?
No, cybersecurity and cloud security are not the same:
Cybersecurity is a broad domain that includes securing all types of IT infrastructure, networks, applications, and data, regardless of where they are hosted.
Cloud Security is a specialized area within cybersecurity focused on protecting data, applications, and services in cloud environments like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure.
While cloud security is a subset of cybersecurity, its tools and strategies are tailored to address cloud-specific challenges such as multi-tenant vulnerabilities and API security.
If you’re ready to take the next step in your cybersecurity journey? You can do that with an expert beside you to guide you through without having to stress much. Schedule a one-on-one consultation with Tolulope Michael, a cybersecurity professional with over a decade of field experience. This will allow you to gain personalized insights and guidance tailored to your career goals.
Visit tolumichael.com now to book your session. This is your opportunity to embark on your cybersecurity career with confidence.
